Many classes have shortcut names used when creating (instantiating) a class with a
configuration object. The shortcut name is referred to as an alias (or xtype if the
class extends Ext.Component). The alias/xtype is listed next to the class name of
applicable classes for quick reference.
Framework classes or their members may be specified as private or protected. Else,
the class / member is public. Public, protected, and private are access
descriptors used to convey how and when the class or class member should be used.
Public classes and class members are available for use by any other class or application code and may be relied upon as a stable and persistent within major product versions. Public classes and members may safely be extended via a subclass.
Protected class members are stable public members intended to be used by the
owning class or its subclasses. Protected members may safely be extended via a subclass.
Private classes and class members are used internally by the framework and are not intended to be used by application developers. Private classes and members may change or be omitted from the framework at any time without notice and should not be relied upon in application logic.
static label next to the
method name. *See Static below.Below is an example class member that we can disect to show the syntax of a class member (the lookupComponent method as viewed from the Ext.button.Button class in this case).
Let's look at each part of the member row:
lookupComponent in this example)( item ) in this example)Ext.Component in this case). This may be omitted for methods that do not
return anything other than undefined or may display as multiple possible values
separated by a forward slash / signifying that what is returned may depend on the
results of the method call (i.e. a method may return a Component if a get method calls is
successful or false if unsuccessful which would be displayed as
Ext.Component/Boolean).PROTECTED in
this example - see the Flags section below)Ext.container.Container in this example). The source
class will be displayed as a blue link if the member originates from the current class
and gray if it is inherited from an ancestor or mixed-in class.view source in the example)item : Object in the example).undefined a "Returns" section
will note the type of class or object returned and a description (Ext.Component in the
example)Available since 3.4.0 - not pictured in
the example) just after the member descriptionDefaults to: false)The API documentation uses a number of flags to further commnicate the class member's function and intent. The label may be represented by a text label, an abbreviation, or an icon.
classInstance.method1().method2().etc();false is returned from
an event handler- Indicates a framework class
- A singleton framework class. *See the singleton flag for more information
- A component-type framework class (any class within the Ext JS framework that extends Ext.Component)
- Indicates that the class, member, or guide is new in the currently viewed version
- Indicates a class member of type config
- Indicates a class member of type property
- Indicates a class member of type
method
- Indicates a class member of type event
- Indicates a class member of type
theme variable
- Indicates a class member of type
theme mixin
- Indicates that the class, member, or guide is new in the currently viewed version
Just below the class name on an API doc page is a row of buttons corresponding to the types of members owned by the current class. Each button shows a count of members by type (this count is updated as filters are applied). Clicking the button will navigate you to that member section. Hovering over the member-type button will reveal a popup menu of all members of that type for quick navigation.
Getting and setter methods that correlate to a class config option will show up in the methods section as well as in the configs section of both the API doc and the member-type menus just beneath the config they work with. The getter and setter method documentation will be found in the config row for easy reference.
Your page history is kept in localstorage and displayed (using the available real estate) just below the top title bar. By default, the only search results shown are the pages matching the product / version you're currently viewing. You can expand what is displayed by clicking on the button on the right-hand side of the history bar and choosing the "All" radio option. This will show all recent pages in the history bar for all products / versions.
Within the history config menu you will also see a listing of your recent page visits. The results are filtered by the "Current Product / Version" and "All" radio options. Clicking on the button will clear the history bar as well as the history kept in local storage.
If "All" is selected in the history config menu the checkbox option for "Show product details in the history bar" will be enabled. When checked, the product/version for each historic page will show alongside the page name in the history bar. Hovering the cursor over the page names in the history bar will also show the product/version as a tooltip.
Both API docs and guides can be searched for using the search field at the top of the page.
On API doc pages there is also a filter input field that filters the member rows using the filter string. In addition to filtering by string you can filter the class members by access level, inheritance, and read only. This is done using the checkboxes at the top of the page.
The checkbox at the bottom of the API class navigation tree filters the class list to include or exclude private classes.
Clicking on an empty search field will show your last 10 searches for quick navigation.
Each API doc page (with the exception of Javascript primitives pages) has a menu view of metadata relating to that class. This metadata view will have one or more of the following:
Ext.button.Button class has an alternate class name of Ext.Button). Alternate class
names are commonly maintained for backward compatibility.Runnable examples (Fiddles) are expanded on a page by default. You can collapse and expand example code blocks individually using the arrow on the top-left of the code block. You can also toggle the collapse state of all examples using the toggle button on the top-right of the page. The toggle-all state will be remembered between page loads.
Class members are collapsed on a page by default. You can expand and collapse members using the arrow icon on the left of the member row or globally using the expand / collapse all toggle button top-right.
Viewing the docs on narrower screens or browsers will result in a view optimized for a smaller form factor. The primary differences between the desktop and "mobile" view are:
The class source can be viewed by clicking on the class name at the top of an API doc page. The source for class members can be viewed by clicking on the "view source" link on the right-hand side of the member row.
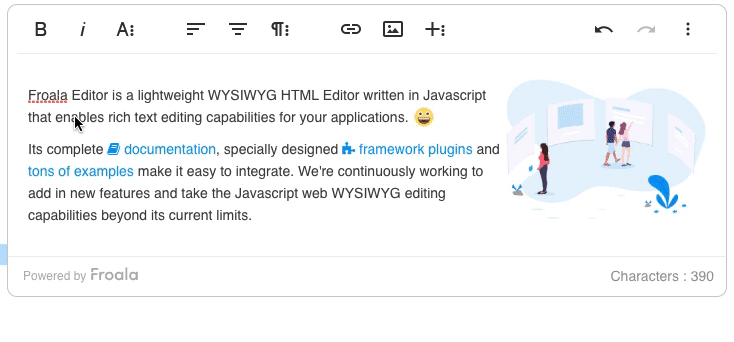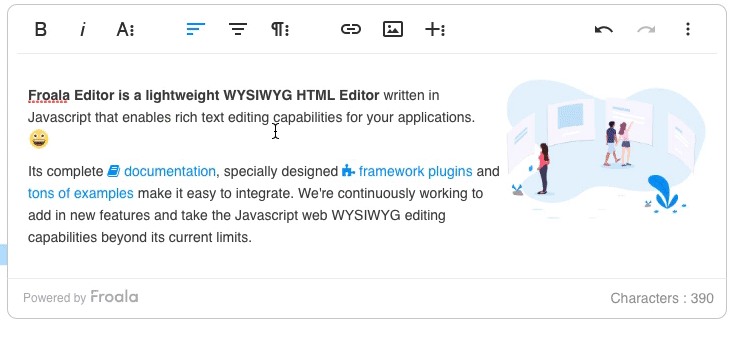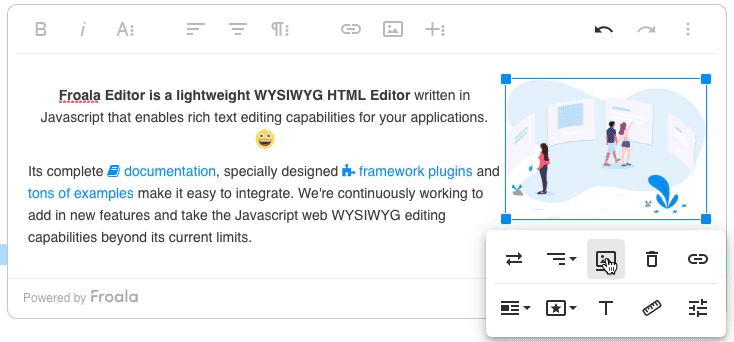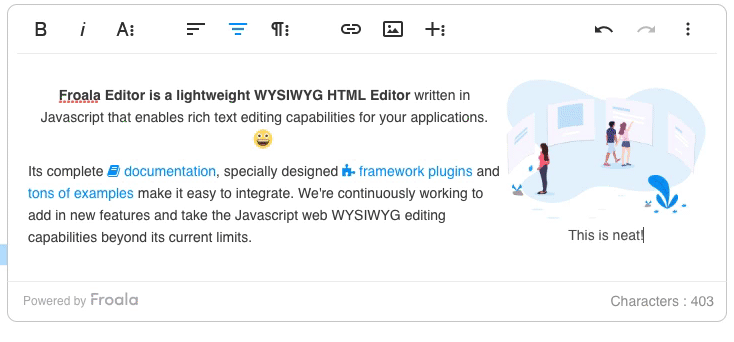
ExtJS 7.x has a Premium code package for Modern toolkit. The package lets you use the Froala WYSIWYG editor within your applications.
There are two versions of the component: a field version, for use in forms, and a regular component version, used anywhere else.
Both classes are simple wrappers around the Froala WYSIWYG editor, documented at https://www.froala.com/wysiwyg-editor. These are ExtJS components, so you can use them like any other component, including setting up listeners to detect component events and Froala native events. You can also run native Froala methods directly on the Froala instance.
The Froala code package is available via Open Tooling (ext-gen) as an npm package as well as a Sencha Cmd package hosted on Sencha's CDN.
Links to detailed installation steps are given below, but in a nutshell you must:
npm login --registry=https://npm.sencha.com --scope=@senchaext-gen project and run npm install @sencha/ext-froala-editorConfigure your app to use the new code package by updating your app's app.json.
In the app.json add froala-editor to the requires array.
{
// ...
"requires": [
"font-awesome",
"froala-editor"
],
// ...
For details on npm repo login see Login to the npm repository.
app.json requires array to include the packageYou have to add the Froala path to the workspace.json packages.dir string:
"packages": {
"dir": "...,${workspace.dir}/node_modules/@sencha/ext-froala-editor",
...
}
There are two versions of the Froala Editor:
Ext.froala.EditorExt.froala.EditorFieldThese components are wrappers around a Froala Editor instance. They are configured and used identically,
but the field version extends Ext.field.Field, and consequently, can be given a name and value,
and be used in field panels and form panels.
There are two primary configs: value, which is the HTML value of the editor, and editor, which is the
configuration for the Froala Editor instance being created.
The value config specifies the initial value of the editor. value is bindable and is the default bind
property. Note that value is HTMl and therefore, will contain HTML tags.
Getting the value example:
myFroalaComponent.setValue('Hello world!');
console.log(myFroalaComponent.getValue()); // Logs "<p>Hello world!</p>"
Simple example:
Within a form you can use the field version. Its name-value pair will be reflected in form submits, or when
calling getValue() on the form.
The editor config lets you configure the Froala editor instance. You can use any Froala config,
as documented at Froala Options.
To listen to events, use the standard listeners component config. You can listen to native Froala events
by using the froala prefix on the event name. Froala events are documented at
Froala Events.
This example shows a Froala editor configured with listener for its change event, and in addition, a listener to the native Froala click event, specified by using the _froala-+ prefix.
To run native Froala methods, use getEditor() to get a reference to the Froala instance, then
run any method you wish. Froala methods are documented at Froala Methods.
For example, to get the character count you'd use this expression:
myFroalaComponent.getEditor().charCounter.count()
When the FroalaEditor or FroalaEditorField is created, it takes a few milliseconds for the wrapped Froala instance
to be created and initialized. When setting up events, this is transparent, but if you need to detect when the instance
is ready, use the ready event. The instance also has an isReady boolean property that starts out false, and changes
to true when the component is initialized.
This code illustrates the relationship between the property and event.
To use a licensed copy of the Froala Editor, you need an activation key, as documented at What is an Activation Key?
Note: The Froala Editor will display a red unlicensed banner when it is deployed to a published site without the activation key. Sencha Enterprise customers can request a free 12-month Froala Enterprise license for use with the Froala component by sending an email to support@froala.com with their Sencha ID/customer account in an email, using "Sencha Ext JS 7.0 Froala Key Request" as the subject line.
You then specify the key in your applications app.json, within a config block named froala. This
is an example that shows a section of app.json with the requires entry for the froala-editor
code package, as well as the specification for the activation key.
{
"name": "MyApp",
"namespace": "MyApp",
"framework": "ext",
"requires": ["font-awesome", "froala-editor"],
"froala": {
"activation-key": "my-activation-key"
}
//...
}